What is Green Tech?

Environmental technology, also known as greentech or cleantech, is the application of environmental science and technology to conserve the natural environment and resources for continued human prosperity.
Goals and Purposes of Greentech/Cleantech
Producers of green technology are striving to achieve this by utilizing renewable energy sources such as the sun, wind, moving water, organic plant material and the earth’s heat. Greentech seeks to identify and replace existing wasteful or harmful habits developed over time to improve the quality of the Earth’s environment and course-correct for a resource-rich future.
- Sustainability: "Sustainability is the ability to exist constantly. In ecology, sustainability is how organisms maintain themselves in one ecological niche for an extended period."
- Cradle-to-cradle design: "Cradle-to-cradle" manufacturing is a method of production that focuses on creating products that can be reused or recycled.
- Innovation: Technology that is commonly used today can have disastrous consequences on the environment, global health and the future of generations to come. Innovation is key to replacing these technologies with more efficient means, through constant research, design and development.
- Viability: The successful implementation of preservation efforts requires the adoption of new methods of green technology, the creation of new careers that facilitate preservation and the design of supportive economic measures that embrace sustainability.
- Source reduction: Source reduction is the term used for reducing waste and pollution by making changes to production methods and resource consumption.
Green technology subject areas are crucial and include things such as environmentally-preferred purchasing, green building, green chemistry, green nanotechnology, and most importantly, green energy production.
GREEN TECHNOLOGY CATEGORIES
The development of alternatives to fossil fuels by discovering new and efficient ways of generating energy is known as green energy.
Green building is the process of creating structures and using processes that are environmentally responsible and resource-efficient throughout a building's life-cycle from siting to design, construction, operation, maintenance, renovation, and demolition.
Green chemistry is the design and implementation of chemical products and processes that eliminate or greatly reduce the use and generation of hazardous substances.
Green nanotechnology is the amalgamation of green chemistry and green engineering principles to create novel materials and production methods.
The environmentally-preferred purchasing method is one in which government entities only purchase products that have been created through energy-efficient means, and those containing non-hazardous materials instead of opting for options that may be more dangerous or less efficient.
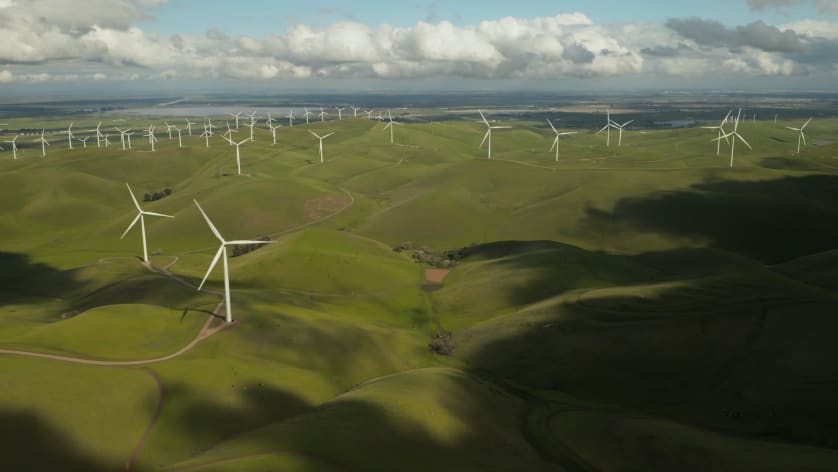
Green Energy Production
The primary purpose of green energy is to generate electricity and power through the utilization of sustainable, naturally occurring energy sources. New greentech is being developed and improved on a regular basis to make better use of consistent resources and harness their strength in hopes of replacing fossil fuels and harmful production methods entirely. Current widespread methods of green energy production include:
- Solar: Solar panels, when combined into a tower and placed in a field or affixed to a roof, work to convert sunlight into electrical energy through photovoltaic components or mirrors that concentrate solar radiation.
- Biogas: Biogas is produced when organic matter breaks down in the absence of oxygen, and is mostly made up of methane and carbon dioxide. Biogas can be compressed and used as a fuel for motor vehicles once the carbon dioxide is removed. Technology is being developed to make use of these gasses on a bigger scale so that we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.
- Geothermal: Geothermal energy is produced by taking advantage of the Earth’s heat just feet below the surface. Temperatures increase by about 1°F every 70 feet, so heat pumps and geothermal systems can be employed to harness this energy for powering and cooling indoor spaces and water.
- Biomass: Biomass can be converted into liquid fuel or oil, creating products that generate electricity or facilitate transportation.
- Nuclear power: Nuclear power is an emission-free energy source that generates electricity through fission, the process of splitting atoms for energy. The heat released by fission creates steam that spins a turbine, generating electricity.
- Low-impact hydroelectric: Low-impact hydroelectric systems that utilize damns, mills, stream-reach applications, and other technologies are needed to extract energy from moving water while minimizing damage to local ecosystems.
Consumer greentech examples
Greentech, also known as environmental technology, is the application of one or more of environmental science, green chemistry, and ecology to develop solutions and mitigate problems caused by human activity.
- Solar panels: The installation of solar panels on homes has become a popular way to generate electricity, as the initial cost of solar panels has decreased.
- Electric vehicles: The use of hybrid and electric vehicles has grown significantly in recent years, helping to reduce pollution from gas vehicles.
- Lithium-ion batteries: These types of batteries are rechargeable and can be used multiple times. The downside to lithium batteries is the fire risk they present and the heavy metals they contain which do not break down. Alkaline batteries, on the other hand, must be replaced more often but don't contain these metals.
- Cloud storage: Advancements in technology have resulted in more efficient computing; however, this process can still require non-renewable resources and consume a great deal of electricity. One of the most influential innovations was the creation of cloud storage, which allows users to store an almost limitless amount of data on highly secure third-party servers designed for fast access from any location. By consolidating these power-drawing computing networks to a limited number of distributed locations, this eliminates the need for having massive amounts of power or storage on hand.
- Smart power bars: By featuring specially designed outlets that restrict the power being used unless the outlet registers an “on” signal from the appliance, smart power bars help to combat the issue of computer and other home appliances still drawing massive amounts of power even when they appear to be inactive.
- Programmable thermostats: Smart thermostats can be used to change the temperature of a home at any time, reducing the use of fossil fuels and electricity.